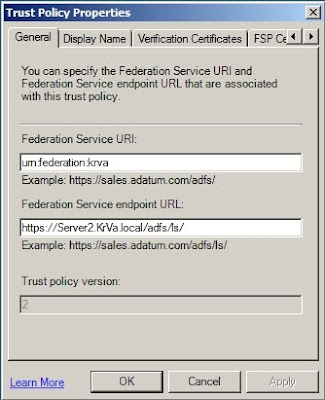
Now that we have our CA installed in the domain, we can configure a member server to act as a Network Protection Server. To do so, several steps will have to be followed again.
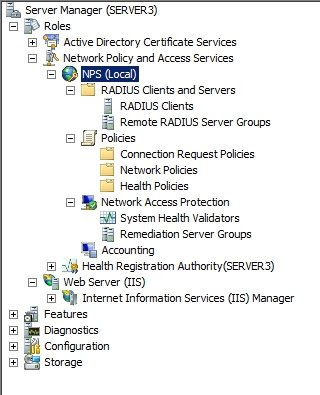
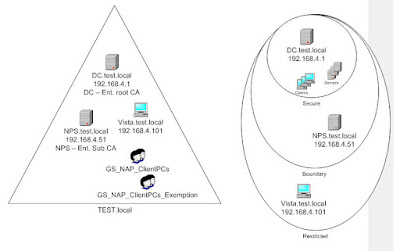
Step 1: Install and configure the NPS: In my case, that would mean the “NPS.test.local” machine:
Install WS08, configure the TCP/IP properties, join to the domain: I don’t suppose this will cause too many problems
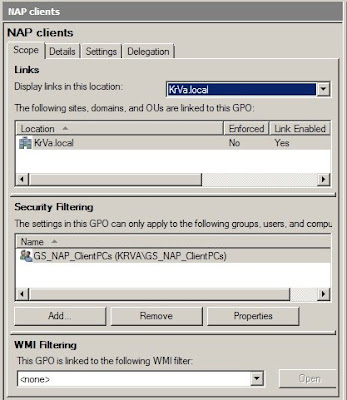
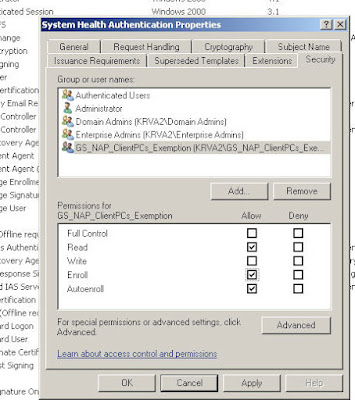
Step 2: Exemption group: since the NPS needs to be able to communicate immediately with all computers on the network, it needs to have a health certificate (without any questions asked :)), so we need to add the computer account to the exemption group created earlier. In my case that would be
NPS.test.local --> GS_NAP_ClientPCs_Exemption. Then restart the NPS server
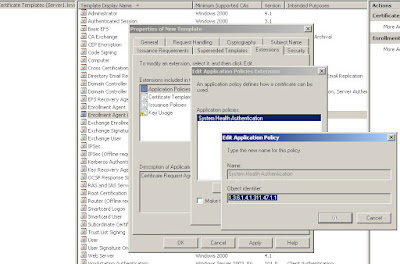
Step 3: Computer certificate: to be able to install the NAP server roles, the computer already needs to have a personal computer certificate. In a
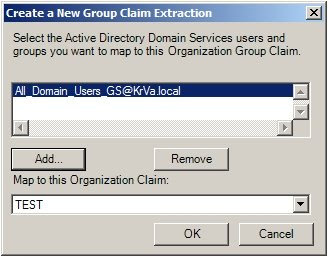
MMC add the certificates of the local computer,
request and enroll a new certificate (computer check box only!).
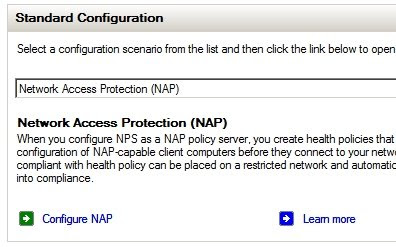
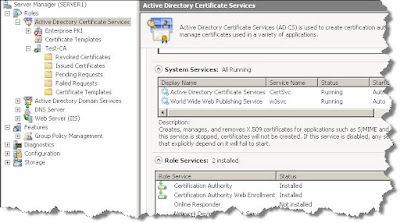
 Step 4: Install NPS, HRA and CA:
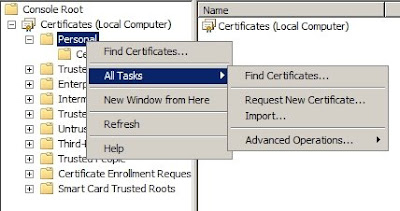
Step 4: Install NPS, HRA and CA: now we can install the NAP server roles
4a CS: in the server roles section, select
Active Directory Certificate Services and
Network Policy and Access Services, then choose
Health Registration Authority, and in the next screen select
Install a local CA.
OK, now this is important, select in the wizard still, select
No, allow anonymous requests for health certificates. This way, computers in a workgroup will be auto-enroleld with health certificates, otherwise they can't be given the certificate automatically! After that, choose to use the
existing certificate to close of the NPS section of the wizard.

Next, we get to the CS part, here select a
Standalone CA, then
Subordinate CA, then
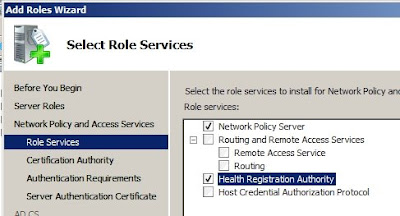
Create a new private key, and Configure the private key and give a clear common name to your CA.
Since this is a subCA, we will have to send the certificate request to the root CA.
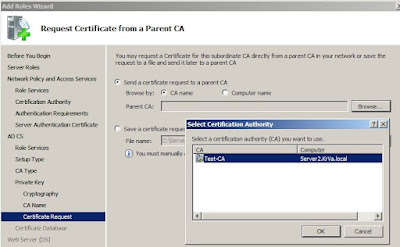
No other settings have to be configured in the wizard, so proceed to the
Install section and verify that the installation was successful.
NOTE: the failure of the HRA section is normal, it will be configured with the correct CA settings in the next steps.
4b: GPMC: Install the Group Policy Management Console via the server
Features.
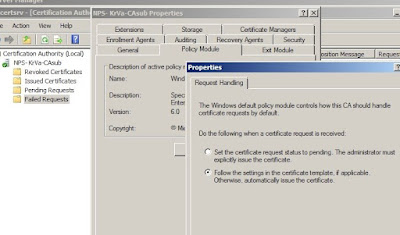
4c: Configure the subCA: now that the Certificate Services are installed we can configure them. Open the CA console and open the Properties
of the subCA. On the tab
Policy Module, open the
Properties and select
Follow the settings in the certificate template, if applicable. Otherwise, automatically issue the certificate. As indicated by the server, stop and restart the CA service.
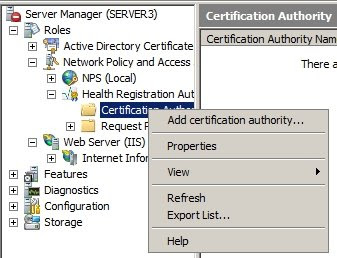
 4d: Configure the CA on Health Registration AuthorityOpen the CA in the HRA console
4d: Configure the CA on Health Registration AuthorityOpen the CA in the HRA console of the
server manager, select to
Add Certification Authority and browse to the subCA.
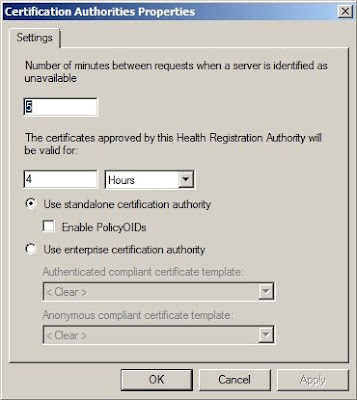
Next, open the
Properties of the
Certification Authority and verify that the settings are as indicated in the screenshot.
That's it for the installation of the NPS itself. In the next post, we'll be configuring the NPS as a NAP Health Policy Server. But the biggest part of the job is done now. As you can see, no rocket science.
Network Address Protection (NAP) posts:
IPsec NAP: Network Address Protection in Server 2008Configuring IPsec NAP (Network Address Protection) - Part 1: CertificatesConfiguring IPsec NAP (Network Address Protection) - Part 3: Configuring the NPS as NAP HRA (Health Registration Authority)Configuring IPsec NAP (Network Address Protection) - Part 4: Testing with a NAP client